Windows Drivers
Note: this driver type is available for Windows only.
Windows drivers allow for low latency. Multichannel recording and playback is possible as well, provided the sound device driver supports this (Pro edition only).
 |
Audio
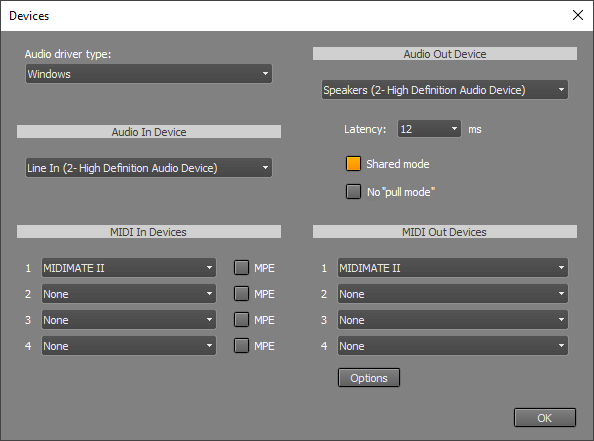
In the Audio In Device section, you can select the audio device that will be used for recording. In the Audio Out Device section, you can select the audio device that will be used for playback. It's a good idea to use Audio In and Out devices that are on the same sound device. If they're not, their sample rates probably won't match exactly. Recorded tracks can therefore gradually become out of sync during playback.
Audio devices are opened in exclusive mode to ensure low latency. This means other programs can't use these audio devices while MultitrackStudio is running.
In Windows 10 (or newer), you can make the Audio Out Device operate in shared mode using the Shared mode button. Shared mode allows other programs to play back audio while MultitrackStudio is running. Latency will be a bit higher, depending on the audio driver. MultitrackStudio will automatically revert to exclusive mode if shared mode can't be used for any reason.
The Latency box determines the time it takes before you hear the sound when playing software instruments live or when using Soft Monitoring ('live effects'). You'll hear glitches if this setting is too low. MultitrackStudio is designed to prevent these glitches from being recorded: if, for example, you record the Guitar Amp effect live with low latency and hear glitches while recording, the glitches won't be in the track, and it will sound fine during playback.
Your sound device may not support low latency values. The actual latency appears if you hover the mouse over the Studio menu's Devices option.
The No "pull mode" button disables "pull mode" (also known as "event mode"). "Pull mode" generally performs better, especially when CPU usage is high. You shouldn't need to disable it on Windows 10 or newer. If you do, you might want to check if there's a better driver available for your device.
MIDI
In the MIDI In Devices section, you can select the device used for MIDI recording.
In the MIDI Out Devices section, you can select the device used for MIDI playback.
Audio Output Control
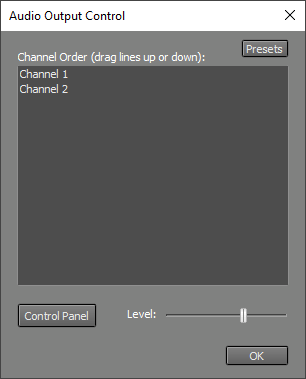 |
The Level fader, available only if the sound device supports it, controls the playback level.
The Control Panel button opens the audio page of the Windows Control Panel, where you can adjust detailed playback levels and other settings, if supported by the sound device.
Under the hood
Windows Vista introduced a new low-latency driver model called WASAPI or "Core Audio". This is what MultitrackStudio uses. Sometimes the term WaveRT is used as well, although this actually refers to a technology used by drivers internally. Windows Vista also introduced MMCSS (Multimedia Class Scheduler Service), which helps prevent audio glitches under high CPU load.